Download of Sample Document:
Paper Title (24 pt, Bold, Title Case)
Name of 1st Author 1, Name of 2nd Author 2 (16 pt, Bold, Title Case)
1 Designation of 1st Author, Name of Department of 1st Author, Name of Organization of 1st Author
2 Designation of 2nd Author, Name of Department of 2nd Author, Name of Organization of 2nd Author
Abstract
This document is a template to provide guidance about formatting the research papers which are going to be submitted to the journal IJFMR. Authors can get a general idea of formatting and various possible sections in the research paper.
“Abstract” is a necessary section in a research paper. It may be constructed by gathering main points (summary) from each section of the research paper.
Keywords: Keyword 1, Keyword 2, Keyword 3
Introduction
- Research paper document file must be of .docx (Microsoft Office Word 2007+) format or .odt (Open Document Text (default document format of LibreOffice / OpenOffice)).
- Whole file must be editable, there must not be any locked/protected region in the document file.
- Set paper/page size to A4.
- It would be better not to use special characters (symbols) in paper’s title, abstract and keywords.
- Write the research paper’s title and keywords in Title Case (capitalize first character of each word). However, write common words like a, an, the, using, for, among etc. in lower case in both title and keywords.
- Use “Times New Roman” font in the whole document. However, programming code may be in a monospaced font; Consolas font is preferred for monospaced content.
- Set alignment “Justify” for all normal paragraphs. Align the figures and tables, and their captions at center. Set left align for the list of references.)
- Except paper’s title and authors’ names, apply 12 pt font to the whole document’s content.
- Avoid using Roman numbers anywhere.
- Avoid Italic style.
- Document need to be in single column layout.
- Set 1.60 cm left and right page margin, and set 1.20 cm top margin, and set 0.60 cm bottom margin.
- Do not give after or before margins to paragraphs; instead, add empty paragraph between two paragraphs to make them separate.
- No first line indent for any paragraph except numbered or bulleted paragraphs. Set “Before Text Indent” to the size of approx 3 spaces between text and numbering/bullets for numbered/bulleted paragraphs.
- Set line spacing to 1.15 everywhere.
- If index of content is added then use the word processor’s tool/feature to create the index. (The tool/feature automatically generates the index of content based on the headings. Index of content generated with this tool keeps the page numbers updated even if headings’ page change because of change in formatting or insertion/deletion of content.)
- Do not add page breaks.
- A parenthetical “statement” at the end of a sentence is punctuated outside of the closing parenthesis (like this). (A parenthetical “sentence” is punctuated within the parentheses.) Similarly, whether to put a punctuation mark at within quotes or after closing quote depends on the quote/sentence; if the text is part of a sentence then put the end punctuation mark after closing quotation mark; and if the quoted text is an independent sentence then put punctuation mark inside the quotation marks.
- It is better to write in passive voice; for example, instead of “We observed that … ”, use “It is observed that … ”.
- Before submitting your research paper, please get it proof-read, by a person having good command over the language used, for spelling and grammatical mistakes, and proper punctuation marks. Authors will be asked to correct the mistakes if there are low amount of mistakes; but research paper will be rejected if there are too many mistakes.
- Paragraph(s) of Conclusion is not necessary, however it is preferred. One should not replicate the content of Abstract in the Conclusion section.
1 Prepare Your Paper Before Styling
- Before you begin to format your paper, first write and save the content as a separate text
- Keep your text and graphic files separate until the text has been formatted and
- There should not be 2 or more spaces or blank lines consecutively in the document.
- Do not use hard tabs; use indentation.
- Finally, complete content and organizational editing before
2. Abbreviations and Acronyms
Define abbreviations and acronyms the first time they are used in the text, even after they have been defined in the abstract.
3. Units
- Use either SI or CGS as primary (SI units are preferred.) English units may be used as secondary units (in parentheses). An exception would be the use of English units as identifiers in trade, such as “3.5 inch disk drive”.
- Avoid combining SI and CGS units, such as current in ampere and magnetic field in This often leads to confusion because equations do not balance dimensionally. If you must use mixed units, clearly state the units for each quantity that you use in an equation.
- Do not mix complete spellings and abbreviations of units: “Wb/m2” or “webers per square meter”, not “webers/m2”. Spell out units when they appear in text: “. . . a few henries”, not “. . . a few H”.
- Use “cm3”, not “cc”.
- Add space between amount and unit; for example – use “12 cm” instead of “12cm”.
- Use upper or lower case properly according to the unit.
1. Equations- Use equation editor feature of your word processing software to create equation if equation contains division, or multiple lines.
- Equations should be left aligned.
- It would be better to give serial numbers for the Equation serial numbers, within parentheses, can be put after half the width of the page.
- If there are multiple equations, and serial numbers are assigned to them, then position all the equation serial numbers at a same tab stop.
- Do not give italic style to equations.
- Use × sign/character for multiplication sign (instead of *), and ÷ sign/character for division sign (instead of /) in equations which are not inserted using an equation editor.
- Add a blank paragraph before and after each equation.
- Use same font size as normal paragraph for the equations.
- Use a zero before decimal points: “25”, not “.25”.
- (a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab
1. Headings
- Headings to be formatted with same font family and font size as normal text.
- Only apply bold style to the headings; no underline, no italic.
- Headings can be numbered or without numbering. It is recommended to use only numbers for numbered heading – means – do not use Roman and Alphabets for numbering headings. Hierarchical numbering (for example – 1.1, 1.1.2) may be used for sub-headings.
- Set “Keep with next paragraph” checkbox checked in the paragraph’s settings/options for all the headings, to avoid heading in one page and its content on the next page.
- Do not add colon at the end of the headings.
2. Figures and Tables
- Add captions/headings for figures and table using their “caption” option/setting.
- Do not format captions with bold or italic or underline style; use same style as normal paragraphs.
- Do not apply background color(s) to cells/rows/columns of tables.
- Center align figures, tables and captions.
- It would be better to give numbers to figures and tables.
- Use Title Case for the captions.
- Set height and width of the cells in tables to minimum required. Tables should be “fit to content”.
- It would be better to provide caption above the figures and tables rather than below them.
- Instead of using short text like “ 1”, use full text like “Figure 1” in captions.
- If figures or images are smaller than half the width of the page then multiple consecutive figures and images may be put in one line. Use table to add multiple figures or images in one line/row.
- Do not write text in the same line as of any figure or table (no wrap).
- Set “bold” style for the column/row headings and footer in the table.
- Use same font size as normal paragraphs for tables’ content. However, if table is wider than the available space in the page then set 10 pt font size for the table’s content. If table is wider even after setting 10 pt font size then authors may consider breaking the table.
- Specify height and width in the same original proportions for images – they shouldn’t be stretched or squeezed disproportionally. And images need to be clear with fine resolution.
- Add blank paragraphs above and below the figures and tables.
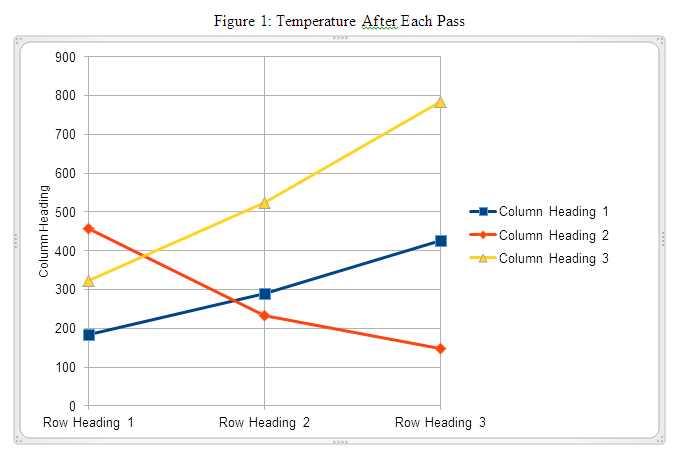
- Table 1: Table Type Styles
-
Column Heading 1 Column Heading 2 Column Heading 3 Row Heading 1 184 456 323 Row Heading 2 290 234 523 Row Heading 3 427 149 785 Total 901 839 1631
- The above data is pictured in the next graph.
1. Some Common Mistakes
- Using 0 (Zero) or O with superscript formatting for the degree symbol used for temperature (Celsius/Fahrenheit), angle (including latitude-longitude). (Proper usage: Use the degree symbol: °.)
- Add a full-stop/period after “et”. (Proper usage: There is no period after the “et” in the Latin abbreviation “et ”.)
- Improper use of “e.” and “e.g.”. (Proper usage: The abbreviation “i.e.” means “that is”, and the abbreviation “e.g.” means “for example”.)
2. Appendix
This section may be added immediately after main content, before acknowledgment, authors’ biography and references.
3. Conflict of Interest
Authors need to add this section if the research was sponsored, or any other way the research was – influenced by anybody/any organization – not fully neutral. Authors must clarify that whether the results of the research were affected by sponsors/influencers or not. If there is no conflict of interest with anybody/any organization then this section is not required.
4. Acknowledgement
Put applicable sponsors acknowledgements in this section; do not place them on the first page of your paper or as a foot-note. Guide’s name may be put either here or on the first page. Other supportive people’s names can be mentioned in this section.
5. Authors’ Biography
Short biography of each author may be included, with/without photographs, after main content of the research paper and before references. The biography may only include details related to current position/designation of the authors. No personal detail can be included in biography
1. References
References within Main Content of the Research Paper
- Enclose the citation number in square brackets, for example: [1].
- Where appropriate, include the names of authors and publication year of the referenced research paper or book, enclosed within round bracket; e.g.: (Rupert Wesley, 2017)
- The reference numbers need to be within same referenced text sentence; i.e., the reference numbers must be before full stop mark of the sentence.
- Multiple reference numbers can be provided in one square bracket: [1, 2]. Add a comma and a space between each reference numbers.
- When referring to a reference, if you want to use its reference number then, do not use “ [3]” or “reference [3]”; only write reference number like this: “[3]”.
- Do not use reference citations as nouns of a sentence; e.g., not “as the author explains in [1]”, specify “as Rupert Wesley (2017) explains”.
- If there are more than one author, write only one author’s name, and use “et al.” for other authors; e.g., (Rupert Wesley, et al., 2017).
- If multiple references can be linked with above format then write other author(s) names to distinguish the references.
References in the Reference List at the End of the Research Paper
- Reference’ details may be added in foot-note (at the end of the page on which reference is mentioned) or in end-note (at the end of the research paper). Either use foot-note or end-not, do not mix. Use end-note if any of the references is referred in more than one paragraphs. End-note is most preferred for list of references.
- Use “1.” numbering format.
- Do not format any part of the reference with italic style.
- There must not be any broken link.
- If website address is provided, it must link/point to the exact research paper or book, i.e., do not just provide www.xyzsite.com; provide full URL with “http://” or “https://” and the path to the exact page like https://www.xyzsite.com/books/path/to/book/abc-book. Write URL after all other details of the reference.
- Separate each part (authors’ names, title, edition, publisher’s name, (month and) year of publication, volume number, issue number, pages to-from) of a reference with commas. Write full-stop at the end of each reference. However, if there is a URL, then write full-stop before the URL. And do not write full-stop after the URL.
- Research papers that have not been published, even if they have been submitted for publication, should be cited as “(unpublished)” [4].
- Research papers that have been submitted for publication, but waiting for being accepted or rejected, should be cited as “submitted for publication”.
- Research papers that have been accepted for publication, but not yet specified for an issue or haven’t been published, should be cited as “to be published”.
- Titles of referenced articles need to be either in the Title Case or Sentence case. Do not write any title only in UPPER CASE or only in lower case.
- Any of the below format may be used for authors names (please be consistent for all references) (4th format is most preferred):
- Roger Robert Federer, Leonardo Wilhelm DiCaprio, Donald John Trump
- Roger R. Federer, Leonardo W. DiCaprio, Donald J. Trump
- Roger F., Leonardo D., Donald T.
- Roger R.F., Leonardo W.D., Donald J.T.
- R. Federer, L.W. DiCaprio, D.J. Trump
- Federer, L. DiCaprio, D. Trump
- Please follow these when specifying names of the authors:
- The first name first, then a space (only if the first character of the middle name isn’t given, full middle name is given or no middle name is given), then optionally middle name, then a space, then the last name.
- No comma between first name, middle name and last name of each author.
- Separate the authors’ names with a comma and a space. Do not write “and” before the last author’s name.
- Please do not write journal/publisher’s name with abbreviations, write full name; or acronym may be used if the publisher is well-known with the acronym.
Example of List of References
- Roger R.F., Leonardo W.D., Donald J.T., “Title of Our Research Paper”, Name of the Publisher/Journal, April 2015, 7 (3), 129–1
- Jack C.M., “Electromagnetic Effects on the Different Kinds of Water”, Journal of Electromagnetic Effects, 1992, 2 (4), 47–76.
- Samuel , “Fine Particles, Thin Films and Exchange Anisotropy”, Magnetism, 1963, 3 (1), 271–350.
- Kate , Title of the Research Paper. (Unpublished)
- Andrew S. “Effect of Non-visible Electromagnetic Particles on Photosynthesis”. https://www.example.com/volume-14/issue-5/effect-of-non-visible-electromagnetic-particles-on-photosynthesis